How to Train a Text Classification Model with trax
ML
What is the trax deep learning framework
trax is coming out of the Google Brain team and is the latest iteration after almost a decade of work on TensorFlow, machine translation, and Tensor2Tensor. Being a new-comer in a somewhat crowded space (keras, pytorch, thinc), it has been able to learn from those APIs.
In particular:
- it is very concise
- it runs on
TensorFlowbackend - it uses
Jaxto speed up tensor-based computation (instead of numpy)
Text Classification on the AG News Dataset
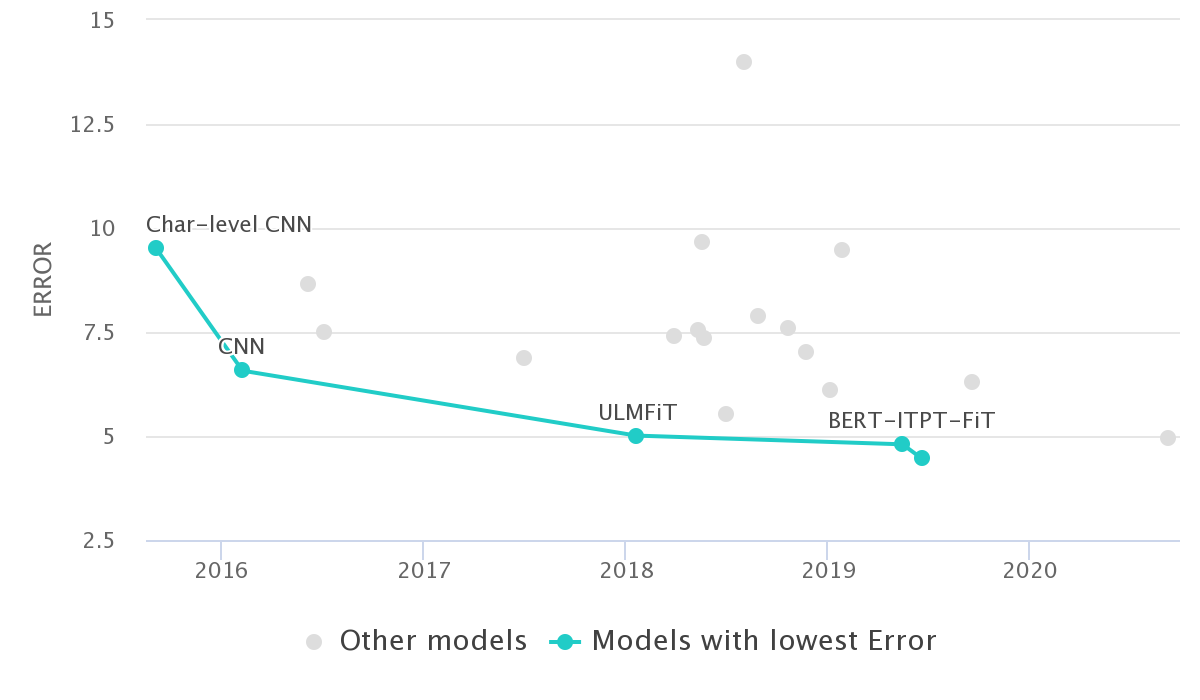
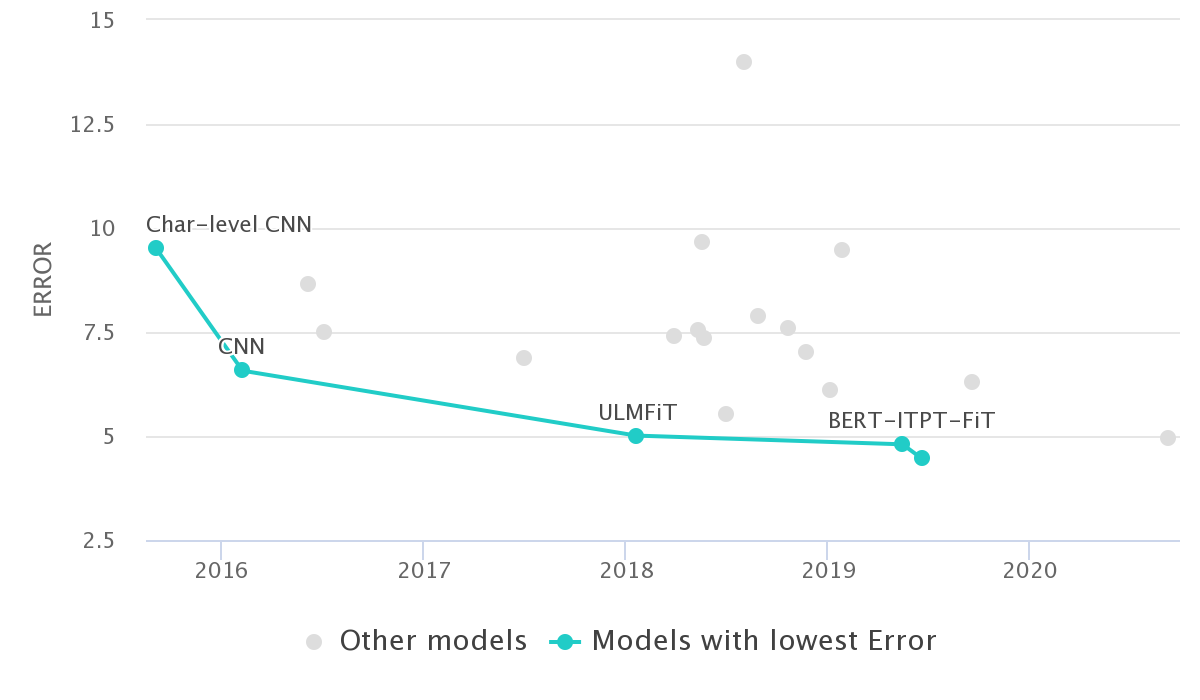
The AG's news topic classification dataset is a dataset of 120,000 training samples of news articles that are of one of 4 classes.
It has been used as a text classification benchmark in numerous papers, like [1509.01626]. You can see the papers using that dataset on paperswithcode.com
On top of being a well-understood dataset, it has the advantage of being available on TensorFlow Datasets. Therefore we will use it in the rest of this post.
Prepare the dataset using trax.data.TFDS and data.Serial
trax needs generators of data. Each element is a tuple (input, target) or (input, target, weight) (usually weight is =1 because all examples have the same importance).
train_stream = data.TFDS(
'ag_news_subset',
keys=('description', 'label'),
train=True
)()
eval_stream = data.TFDS(
'ag_news_subset',
keys=('description', 'label'),
train=False
)()
data_pipeline = data.Serial(
data.Tokenize(vocab_file='en_8k.subword', keys=[0]),
data.Shuffle(),
data.FilterByLength(max_length=2048, length_keys=[0]),
data.BucketByLength(boundaries=[ 32, 128, 512, 2048],
batch_sizes=[512, 128, 32, 8, 1],
length_keys=[0]),
data.AddLossWeights()
)
train_batches_stream = data_pipeline(train_stream)
eval_batches_stream = data_pipeline(eval_stream)
Build the Text Classification Model using tl.Serial
trax is really concise, you can use the library of layers available.
model = tl.Serial(
tl.Embedding(vocab_size=8192, d_feature=50),
tl.Mean(axis=1),
tl.Dense(4),
tl.LogSoftmax()
)
Model Training using training.Loop
For training, there is the concept of a "task" which wraps the data, the optimiser, the metrics etc...
# Training task.
train_task = training.TrainTask(
labeled_data=train_batches_stream,
loss_layer=tl.CrossEntropyLoss(),
optimizer=trax.optimizers.Adam(0.01),
n_steps_per_checkpoint=500,
)
# Evaluaton task.
eval_task = training.EvalTask(
labeled_data=eval_batches_stream,
metrics=[tl.CrossEntropyLoss(), tl.Accuracy()],
n_eval_batches=20 # For less variance in eval numbers.
)
# Training loop saves checkpoints to output_dir.
output_dir = os.path.expanduser('~/output-dir/')
!rm -rf {output_dir}
training_loop = training.Loop(model,
train_task,
eval_tasks=[eval_task],
output_dir=output_dir)
# Run 2000 steps (batches).
training_loop.run(2000)
Look at the Predictions
inputs, targets, weights = next(eval_batches_stream)
example_input = inputs[0]
expected_class = targets[0]
example_input_str = trax.data.detokenize(example_input, vocab_file='en_8k.subword')
print(f'example input_str: {example_input_str}')
sentiment_log_probs = model(example_input[None, :]) # Add batch dimension.
print(f'Model returned class probabilities: {np.exp(sentiment_log_probs)}')
print(f'Expected class: {expected_class}')